The second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity.The first law places no restriction on the direction of a process, and satisfying the first law does not guarantee that the process will occur. Thus, we need another general principle (second law) to identify whether a process can occur or not.
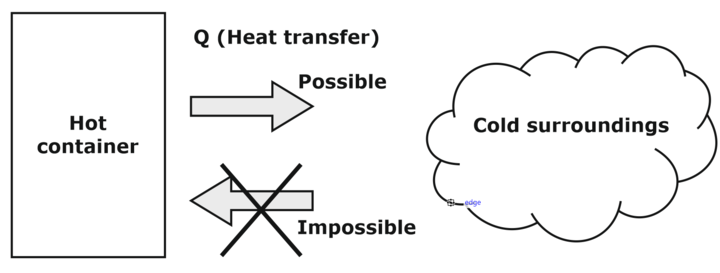
Fig. above shows Heat transfer process can occur when and only when it satisfies both the first and the second laws of thermodynamics.
- The second law also asserts that energy has a quality. Preserving the quality of energy is a major concern of engineers. In the above example, the energy stored in a hot container (higher temperature) has higher quality (ability to work) in comparison with the energy contained (at lower temperature) in the surroundings.
- The second law is also used in determining the theoretical limits for the performance of commonly used engineering systems, such as heat engines and refrigerators etc.m a hot container to the cold surroundings is possible; however, the reveres process (although satisfying the first law) is impossible.
Thermal Energy Reservoirs
- Thermal energy reservoirs are hypothetical bodies with a relatively large thermal energy capacity (mass x specific heat) that can supply or absorb finite amounts of heat without
undergoing any change in temperature. Lakes, rivers, atmosphere, oceans are example of thermal reservoirs. - A two‐phase system can be modeled as a reservoir since it can absorb and release large quantities of heat while remaining at constant temperature.
- A reservoir that supplies energy in the form of heat is called a source and one that absorbs energy in the form of heat is called a sink.
Heat Engines:
- Heat engines convert heat to work. There are several types of heat engines, but they are characterized by the following:
- They all receive heat from a high‐temperature source (oil furnace, nuclear reactor, etc.)
- They convert part of this heat to work
- They reject the remaining waste heat to a low‐temperature sink
- They operate in a cycle
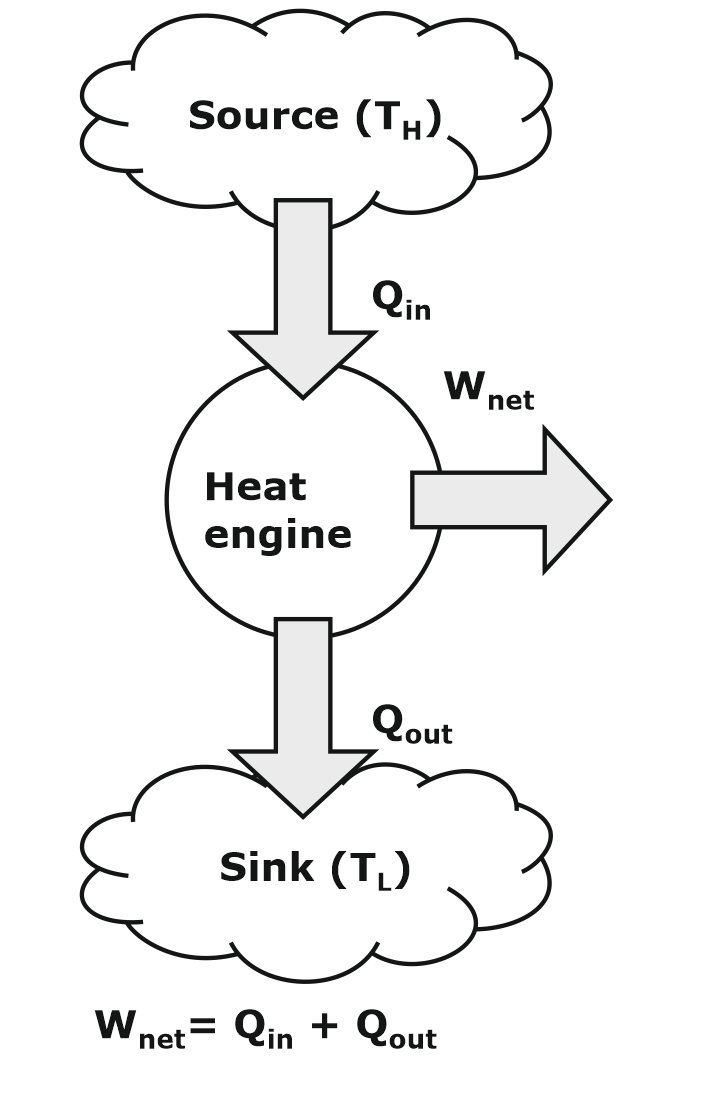
- They all receive heat from a high‐temperature source (oil furnace, nuclear reactor, etc.)
- Thermal efficiency: is the fraction of the heat input that is converted to the net work output (efficiency = benefit/cost).
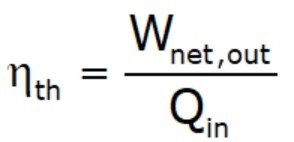
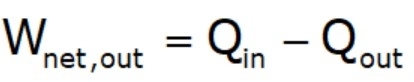
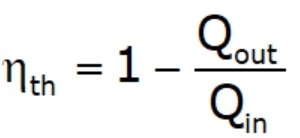
- The thermal efficiencies of work‐producing devices are low. Ordinary spark‐ignition automobile engines have a thermal efficiency of about 20%, diesel engines about 30%, and power plants in the order of 40%.
The Second Law: Kelvin‐Planck Statement
- It is impossible for any device that operates on a cycle to receive heat from a single reservoir and produce a net amount of work. In other words, no heat engine can have a thermal efficiency of 100%.
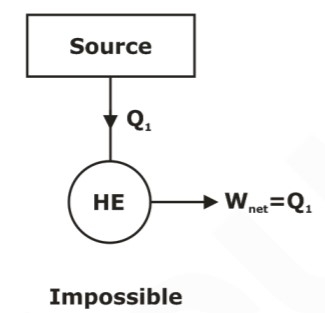
Fig above shows A heat engine that violates the Kelvin‐Planck statement of the second law cannot be built.
Refrigerators and Heat Pumps
- In nature, heat flows from high‐temperature regions to low‐temperature ones. The reverse process, however, cannot occur by itself.
- The transfer of heat from a low‐temperature region to a high‐temperature one requires special devices called refrigerators.
- Refrigerators are cyclic devices, and the working fluids used in the cycles are called refrigerant.
- Heat pumps transfer heat from a low‐temperature medium to a high‐temperature one.
- Refrigerators and heat pumps are essentially the same devices; they differ in their objectives only. Refrigerator is to maintain the refrigerated space at a low temperature.
- On the other hand, a heat pump absorbs heat from a low‐temperature source and supplies the heat to a warmer medium.
Comments
Post a Comment