STRAIN:-
When a prismatic bar is subjected to axial load, it undergoes a change in length, as indicated in Figure. This change in length is usually called deformation.
Or
In simple terms the definition is
The strain is equal to the ratio of change in length of the body to the original length.
If the axial force is tensile, the length of the bar is increased, while if the axial force is compressive, there is shortening of the length of the bar.
The deformation (i.e. elongation or shortening) per unit length of the bar is termed as strain and denoted by ε or e.
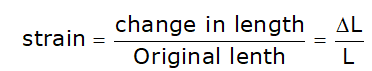
Types of Strain:
(i) Longitudinal strain:
The ratio of axial deformation along the length of the applied load to the original length of the body is known as longitudinal (or linear) strain.
L = Length of the body,
P = Tensile force acting on the body,
δL = Increase in the length of the body in the direction of P.
Then,

(ii) Lateral strain:
The strain at right angles to the direction of applied load is known as lateral strain. Let a rectangular bar of length L, breadth b and depth d is subjected to an axial tensile load P. The length of the bar with increase while the breadth and depth will decrease.
δL = Increase in length,
δb = Decrease in breadth, and
δd = Decrease in depth.
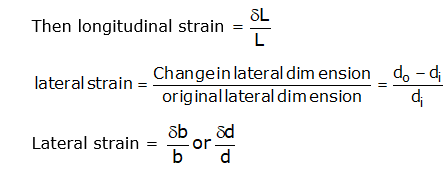





Comments
Post a Comment