ZEROTH LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
It is the basic law of thermodynamics which defines the temperature.
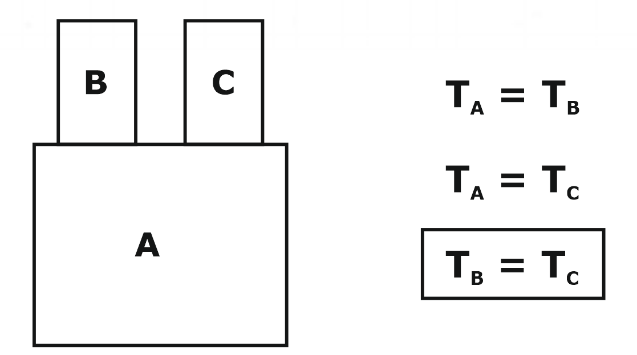
Zeroth law states that:
“When a body A is in thermal equilibrium with a body B, and also separately with a body C, then B and C will be in thermal equilibrium with each other”.
It is the basis of temperature measurement.
THERMOMETRIC PROPERTIES
In order to obtain a quantitative measure of temperature, a reference body is used, and a certain physical characteristic of this body which changes with temperature is selected. The selected characteristic is called the thermometric property, and the reference body which is used in the determination of temperature is called the thermometer.
Variables which are used to determine the temperature is known as Thermometric property.
(i) Constant Volume thermometer – From ideal gas equation
For constant volume, P α T, So T= f(P) Only
i.e. temperature is only dependent on pressure, thus for constant volume thermometer Pressure, P will be thermometric property.
(ii) Constant Pressure thermometer – From ideal gas equation
For constant Pressure, V α T, So T= f(V) Only
i.e. temperature is only dependent on Volume, thus for constant Pressure thermometer Volume, V will be thermometric property.
(iii) In electrical resistance thermometer, resistance will be thermometric property.
(iv) In case of Thermocouple, Voltage or EMF will be thermometric property.
(v) In case of thermometer, length or Volume will be thermometric property.
These all are the linearly varying.
Thus , T =a.N where a is random constant.
& N is the thermometric property
Five different kinds of thermometer, each with its own thermometric property,
ENERGY
(i) Energy in a thermodynamic System can be transferred in three ways namely Work, Heat and By mass.
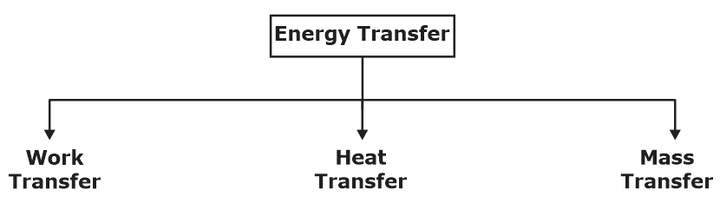
(ii) A closed System and its Surroundings can interact by work transfer and Heat transfer, whereas open system can interact By work, Heat and mass transfer (because mass also carries energy).
FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
First law of thermodynamics is to relate the various form of energy and energy interaction.
Its states that “Energy can be neither created nor destroyed during a process; it can only change forms”.
It is also known as “Conservation of energy principle”
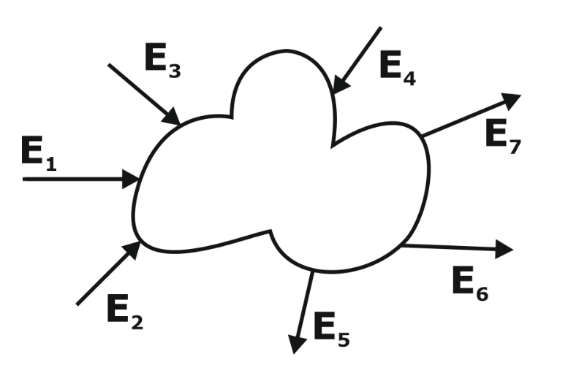
From the above statement we can say that, energy leaving the system must be equal to the energy supplied to the system.
Ein = Eout
FIRST LAW FOR A CLOSED SYSTEM UNDERGOING A CYCLE
As per the first law for closed system undergoing a cycle, net heat interaction in a cycle is equal to the net Work interaction.
where J is the Joule’s equivalent. This is also expressed in the form
Fig.1: Closed System Undergoing A Cycle
1st LAW FOR A CLOSED SYSTEM UNDERGOING A CHANGE OF STATE (for a process)
The expression
applies only to systems undergoing cycles, and the algebraic summation of all energy transfer across system boundaries is zero.
But if a system undergoes a change of state during which both heat transfer and work transfer are involved, the net energy transfer will be stored or accumulated within the system.
If Q is the amount of heat transferred to the system and W is the amount of work transferred from the system during the process
Then, net energy transfer (Q – W) will be stored in the system.
Energy in storage is neither heat nor work, and is given the name internal energy or simply, the energy of the system.
Therefore, Q – W – ΔE
where ΔE is the increase in the energy of the system
Q = ΔE + W
CONSEQUENCES OF 1ST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
(i) Heat is a path function.
(ii) Energy-a property of the system.
(iii) Energy of isolated system is Constant.
(iv) Perpetual motion machine of first kind-PMM1 is not possible.
Comments
Post a Comment